Ecosystem & Ecology: A Detailed Study of Life and Environment
Introduction
The Earth is a complex and dynamic planet filled with diverse forms of life. From microscopic bacteria to giant trees and animals, every living organism plays an important role in maintaining balance in nature. The study of how living organisms interact with one another and with their environment is known as ecology, while the system formed by these interactions is called an ecosystem.
Understanding ecosystem and ecology is essential because they explain how life survives, adapts, and continues on Earth. These concepts help us understand environmental issues such as climate change, pollution, deforestation, and biodiversity loss. In this detailed guide, we will explore the meaning, components, types, functions, and importance of ecosystem and ecology.
What is Ecology?
Ecology is a branch of biology that studies the relationships between living organisms and their physical environment. The term ecology comes from the Greek words oikos meaning home and logos meaning study. Thus, ecology literally means the study of organisms in their home.
Ecologists study how organisms depend on each other for food, shelter, protection, and reproduction. They also examine how environmental factors such as temperature, sunlight, water, and soil affect living beings.
Ecology can be divided into several branches. Autecology is the study of individual species and their relationship with the environment. Synecology focuses on groups of species living together as a community. Population ecology studies population size, growth, and distribution. Community ecology examines interactions among different species in a community. Ecosystem ecology studies energy flow and nutrient cycling. Global ecology deals with large-scale environmental patterns and global changes.
What is an Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with each other and with their non-living environment in a specific area. It includes plants, animals, microorganisms, air, water, soil, sunlight, and climate.
An ecosystem can be as small as a pond or as large as a forest, desert, or ocean. The Earth itself is considered a giant ecosystem called the biosphere.
An ecosystem is the structural and functional unit of nature where living organisms interact with each other and their physical environment.
Components of an Ecosystem
An ecosystem has two main components: biotic components and abiotic components.
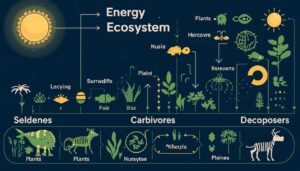
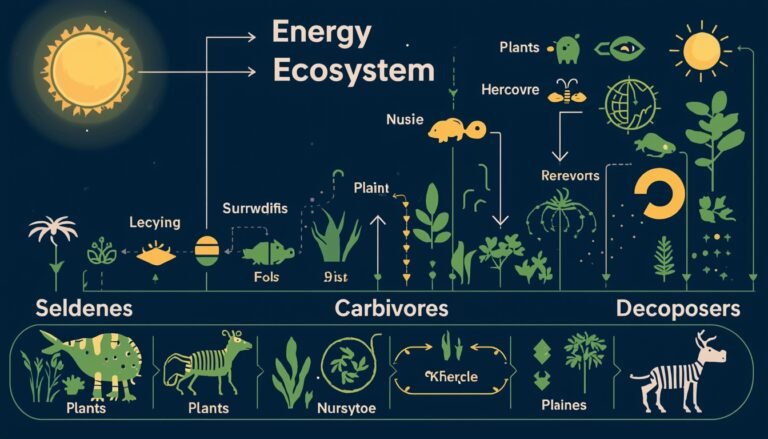
Biotic components include all living organisms in an ecosystem. Producers are green plants and algae that make their own food through photosynthesis using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. They are also called autotrophs. Consumers are organisms that depend on others for food and are called heterotrophs. Primary consumers are herbivores that eat plants. Secondary and tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other animals. Omnivores eat both plants and animals. Decomposers such as bacteria and fungi break down dead plants and animals into simpler substances, returning nutrients to the soil and maintaining ecological balance.
Abiotic components include non-living physical and chemical factors such as sunlight, air, water, soil, temperature, and minerals. These factors influence the survival, growth, and distribution of living organisms.
Types of Ecosystems
Ecosystems can be natural or artificial. Natural ecosystems occur without human intervention. These include terrestrial ecosystems such as forests, deserts, grasslands, and mountains, as well as aquatic ecosystems such as rivers, lakes, ponds, seas, and oceans.
Artificial ecosystems are created and maintained by humans. Examples include gardens, agricultural fields, aquariums, and crop farms. These ecosystems depend on human management for their survival.
Structure of an Ecosystem
The structure of an ecosystem refers to the arrangement of its biotic and abiotic components. It includes species composition, trophic levels, spatial arrangement, and feeding relationships. The interaction between these components determines the stability and productivity of the ecosystem.
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
Energy is the driving force of every ecosystem, and the sun is the primary source of energy. Plants capture solar energy through photosynthesis and convert it into chemical energy stored in food. Herbivores obtain this energy by eating plants. Carnivores get energy by eating herbivores. Decomposers break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients.
Energy flow follows a one-way direction and cannot be reused. At each trophic level, some energy is lost as heat, which is why energy decreases as it moves upward in the food chain.
Food Chain and Food Web
A food chain is a simple linear sequence that shows how energy flows from one organism to another. For example, grass is eaten by a deer, and the deer is eaten by a tiger.
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains. It shows multiple feeding relationships in an ecosystem. Food webs increase ecosystem stability because organisms have alternative food sources.
Ecological Pyramid
An ecological pyramid represents the relationship between organisms at different trophic levels. There are three main types: pyramid of numbers, pyramid of biomass, and pyramid of energy. The pyramid of energy is always upright because energy decreases at each level due to heat loss.
Ecological Balance
Ecological balance refers to the stability between living organisms and their environment. When this balance is disturbed, environmental problems occur. Deforestation, pollution, climate change, overpopulation, and industrialization are major causes of ecological imbalance. Maintaining balance is essential for sustainable development and the survival of all species.
Importance of Ecosystem
Ecosystems provide many essential services that support life. They produce oxygen, provide food, purify water, regulate climate, maintain soil fertility, support pollination, and conserve biodiversity. Without ecosystems, human life and other forms of life would not be possible.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in an ecosystem. A healthy ecosystem usually has high biodiversity. Greater biodiversity increases stability, resistance to disease, and productivity. Loss of biodiversity weakens ecosystems and makes them vulnerable to disturbances.
Human Impact on Ecosystem
Human activities have greatly affected ecosystems. Pollution contaminates air, water, and soil. Deforestation destroys habitats. Urbanization reduces natural spaces. Overfishing threatens marine life. Global warming alters climate patterns. These impacts lead to species extinction and environmental degradation.
Conservation of Ecosystem
Conservation means protecting and managing natural resources responsibly. Methods of conservation include afforestation, wildlife protection, pollution control, sustainable agriculture, and the use of renewable energy sources. Public awareness and government policies play a crucial role in ecosystem conservation.
Difference Between Ecology and Ecosystem
Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and their environment. An ecosystem is the actual system where these interactions occur. In simple terms, ecology is the study, and ecosystem is the system being studied.
Modern Challenges in Ecology
Today, ecologists face many global challenges such as climate change, water scarcity, plastic pollution, deforestation, and species extinction. Scientific research and sustainable environmental practices are necessary to overcome these challenges.
Conclusion
Ecosystem and ecology are fundamental concepts that help us understand the complex relationships between living organisms and their environment. Ecology explains how organisms interact, while an ecosystem represents the natural system where these interactions take place.
Ecosystems support life by providing essential resources such as food, oxygen, and water. However, human activities are disturbing ecological balance, leading to serious environmental issues. Understanding these concepts encourages us to protect nature and adopt sustainable practices.
If we conserve ecosystems today, we ensure a healthy and balanced planet for future generations.
Ecosystem & Ecology – 50 SAQ with Answers
1. What is ecology?
Ecology is the branch of biology that studies interactions between organisms and their environment.
2. What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with their physical environment.
3. Who introduced the term ecology?
Ernst Haeckel introduced the term ecology in 1866.
4. What are biotic components?
Biotic components are the living parts of an ecosystem.
5. What are abiotic components?
Abiotic components are the non-living physical and chemical factors in an ecosystem.
6. Name two abiotic factors.
Sunlight and water.
7. Who are producers in an ecosystem?
Producers are organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis.
8. Give an example of a producer.
Green plants.
9. Who are consumers?
Consumers are organisms that depend on other organisms for food.
10. What are decomposers?
Decomposers are organisms that break down dead matter into simpler substances.
11. Give an example of a decomposer.
Fungi.
12. What is a food chain?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms showing energy transfer.
13. What is a food web?
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains.
14. What is the main source of energy in an ecosystem?
The Sun.
15. What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make food using sunlight.
16. What is ecological balance?
Ecological balance is the stability between organisms and their environment.
17. What is biodiversity?
Biodiversity is the variety of living organisms in an area.
18. Name one terrestrial ecosystem.
Forest ecosystem.
19. Name one aquatic ecosystem.
Marine ecosystem.
20. What is a trophic level?
A trophic level is a position in a food chain.
21. What is a pyramid of energy?
It shows the flow of energy at different trophic levels.
22. Why is the energy pyramid always upright?
Because energy decreases at each level.
23. What is population ecology?
It is the study of population size and growth.
24. What is community ecology?
It is the study of interactions among species in a community.
25. What is autecology?
It is the study of individual species and their environment.
26. What is synecology?
It is the study of groups of species living together.
27. What is the biosphere?
The biosphere is the global ecological system of Earth.
28. What is habitat?
A habitat is the natural home of an organism.
29. What is an artificial ecosystem?
An ecosystem created and maintained by humans.
30. Give an example of an artificial ecosystem.
Aquarium.
31. What is nutrient cycling?
The movement and exchange of nutrients in an ecosystem.
32. What causes ecological imbalance?
Pollution and deforestation.
33. What is global warming?
The rise in Earth's average temperature due to greenhouse gases.
34. What is conservation?
The protection and sustainable use of natural resources.
35. What is deforestation?
The cutting down of forests.
36. What is pollution?
The contamination of the environment by harmful substances.
37. What is a herbivore?
An animal that eats plants.
38. What is a carnivore?
An animal that eats other animals.
39. What is an omnivore?
An organism that eats both plants and animals.
40. What is a climax community?
A stable and mature ecological community.
41. What is succession?
The gradual change in species composition over time.
42. What is primary succession?
Succession that begins in a lifeless area.
43. What is secondary succession?
Succession that occurs after disturbance in an existing ecosystem.
44. What is a biome?
A large ecological region with similar climate and organisms.
45. Name one example of a biome.
Desert biome.
46. What is climate?
The long-term weather pattern of an area.
47. What is ecosystem productivity?
The rate at which energy is converted into biomass.
48. Why are decomposers important?
They recycle nutrients back into the soil.
49. How do humans affect ecosystems?
Through pollution, urbanization, and resource exploitation.
50. Why is ecology important?
Ecology helps us understand and protect the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment.
Ecology is the scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environment.
The term ecology was introduced by Ernst Haeckel in 1866.
Biotic components are the living parts of an ecosystem, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Abiotic components are the non-living parts of an ecosystem like sunlight, water, soil, and climate.
Producers, mainly plants and algae, create food through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food chain.
Consumers are organisms that rely on other organisms for food, including herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores.
Decomposers, like fungi and bacteria, break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
A food chain is a linear sequence showing how energy passes from one organism to another in an ecosystem.
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains, showing multiple feeding relationships in an ecosystem.
Follow Toppers Track for daily updates 📢